Program Structure
The course is characterised by a multidisciplinary and integrated approach to teaching, with a total of 360 credits and 29 exams, distributed into 12 semesters
Among the teaching methods, particular relevance is given to interactive teaching, which mostly consists of group activities coordinated by a tutor. Examples of such methods are Problem Based Learning, Case Method, Concept Maps and Portfolios.
Particular attention is also paid to vocational training in order to promote the acquisition of specific vocational skills. This approach allows students to fully integrate theory and practice, developing a critical and autonomous reasoning.
Study Plan A.Y. 2021/2022
The following study plan is valid for newly enrolled students in the 2021/2022 academic year only.
| Semester | Course Teaching / Modules | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | PRINCIPLES OF THE LIVING MATTER
FIS/07 Medical Physics BIO/10 Chemistry |
9 |
| 1st | BUILDING BODIES
BIO/17 Histology BIO/16 Human Anatomy BIO/17 Cytology |
12 |
| Annual | BEING A MEDICAL DOCTOR
MED/02 History of Medicine M-FIL/03 Bioethics M-PED/01 Pedagogy M-PSI/01 General Psychology M-PSI/08 Clinical Psychology
|
6 |
| 2nd | THE CELL: MOLECULES AND PROCESSES
BIO/13 Applied Biology |
6 |
| 2nd | BODY ARCHITECTURE
BIO/16 Anatomy MED/36 Radiology |
11 |
| 2nd | THE CELL: FUNCTIONS AND CONTROL BIO/10 BiochemistryBIO/09 Human Physiology |
9 |
| 2nd | PROFESSIONALISING ACTIVITIES 1st YEAR
Professionalising Activities |
3 |
| Total | 56 |
Study Plan A.Y. 2020/2021
| Semester | Course Teaching / Modules | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | PRINCIPLES OF THE LIVING MATTER
Medical Physics Chemistry |
9 |
| 1st | BUILDING BODIES
Histology and Embryology Human Anatomy |
11 |
| 1st | BEING A MEDICAL DOCTOR
History of Medicine Bioethics General pedagogy |
4 |
| Annual | THE CELL: MOLECULES AND PROCESSES
Biochemistry Applied biology Cytology Molecular biology Genetics |
19 |
| 2nd | BODY ARCHITECTURE
Human anatomy |
9 |
| Total | 52 |
Teaching and Assessment
There are several types of learning activities including core courses, vocational training, elective courses and training activities for the preparation of the thesis.
For each learning activity, students gain a certain number of university credits and a mark awarded on a 30-point scale or pass/fail exam. The minimum passing mark is 18/30. Any attribution of honor, in addition to the maximum mark of 30, is subject to the unanimous assessment of the Commission.
The assessment is performed through written and oral exams and where pertinent through the student’s portfolio. The clinical skills are assessed through OSCE (Objective Structure Clinical Examination). All exams are taken during specific exam periods.
Core Courses – Integrated teaching
Core courses are held by one or more professors, depending on the specific objectives assigned to each course. For each course, a Coordinator is appointed annually by the Academic Board. The specific objectives of each course are outlined in the syllabuses provided annually by the professors.
Integrated courses are those that include different modules, held by more than one professor. Students can thus gain a complete insight into all the aspects related to each subject. For example, in the “Head and Neck” integrated course students will learn the anatomy and physiology of the head and neck, as well as the related diseases (otorhinolarynogological, odontostomatological and ophtalmological). Continuous assessment may be prescribed for such courses. The marks of continuous assessment converge into one final mark.
Vocational training
This form of tutorial teaching involves performing practical clinical activities under the supervision of a tutor, but with a considerable degree of autonomy, to simulate the activity performed at a professional level. Students are required to acquire practical skills in several fields of medical practice, for a total of 60 credits. The skills acquired during the vocational training are tested through OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination). Vocational training activities may include laboratories for the acquisition of practical and relational skills, briefing and debriefing, formative feedback and portfolio.
Elective courses
Elective activities are learning activities freely chosen by students within a range of proposals offered annually by the teaching body, according to the established methods, procedures and limits of the degree programme. These activities give the student the opportunity to analyse specific or innovative subjects.
Students are also encouraged to attend internal seminars and conferences, participate in research activities and experiences abroad through the Erasmus programme or other international mobility options.
Final examination
To be admitted to the final examination, students must develop an original thesis under the supervision of a professor or tutor. This activity is known as internato di laurea or degree internship.
Eligibility to take the degree exam is subject to successful completion of all the exams required by the study plan for a total of 342 credits.
The final degree mark (out of 110) is determined by:
- final weighed average (out of 110)
- up to 10 points allocated by the Degree Commission
Any award of honors is subject to having achieved a weighted average of at least 102 and depends on the unanimous assessment of the Commission.
18 credits are assigned to thesis preparation
To calculate your weighted average consult the Academic Regulations.
Students can attend elective activities throughout the entire course of study, and must gain 8 credits in the context of elective courses before graduating.
| Credits (CFU) |
|---|
| A university credit (CFU) is the unit of measure of learning work that a student needs for the completion of each course.
1 CFU consists of 25 coursework and workload hours, including at least 50% of study. Each CFU may correspond to:
|
Virgilio Program
The project is funded by Fondazione Cariplo and coordinated by Università degli Studi Milano Bicocca. It is open to students attending Humanitas University, Università degli Studi di Milano and Università degli Studi Milano Bicocca.
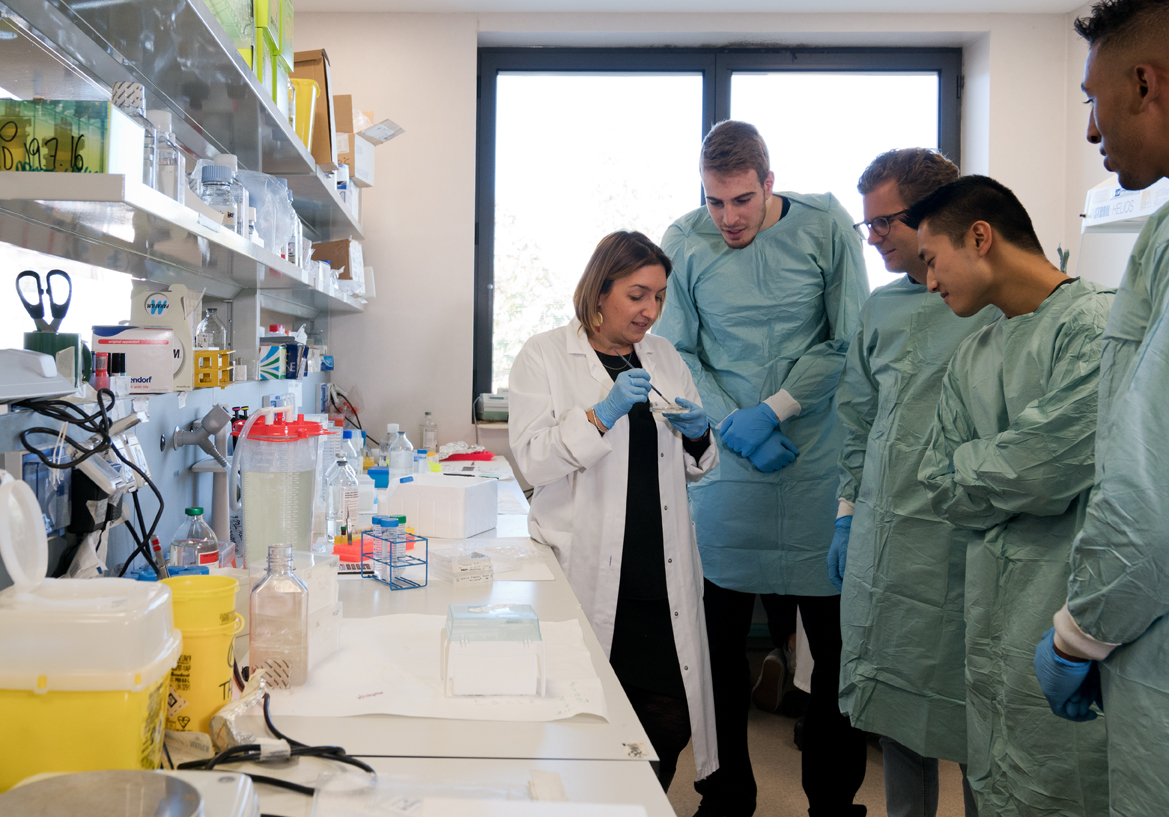
Medical students will develop a deep understanding of the link between basic research and clinical research and be able to combine patient care with biomedical research.
The program, taught entirely in English, is intended for a selected number of third-year medical students, who for three years will integrate their curriculum with inter-disciplinary seminars and internship activities in research laboratories.
In particular, the program allows students to gain 60 additional university credits through seminars, courses and laboratory activities.
A team of mentors and tutors will support the students in all their activities, including the preparation of their thesis and laboratory activities.
Thanks to the collaboration between the three universities and the cooperation of the team of mentors and tutors, students will be able to carry out research activities to complete their experimental thesis in any of the three partner universities.
| Call for Applications a.y. 2025/2026 |
|---|
| Call for Applications a.y. 2025/2026
For any additional information, please visit the Virgilio Program official website. |
| Ranking list a.y. 2025/2026 |
|---|
| The ranking list will be published by 1st June 2025. |